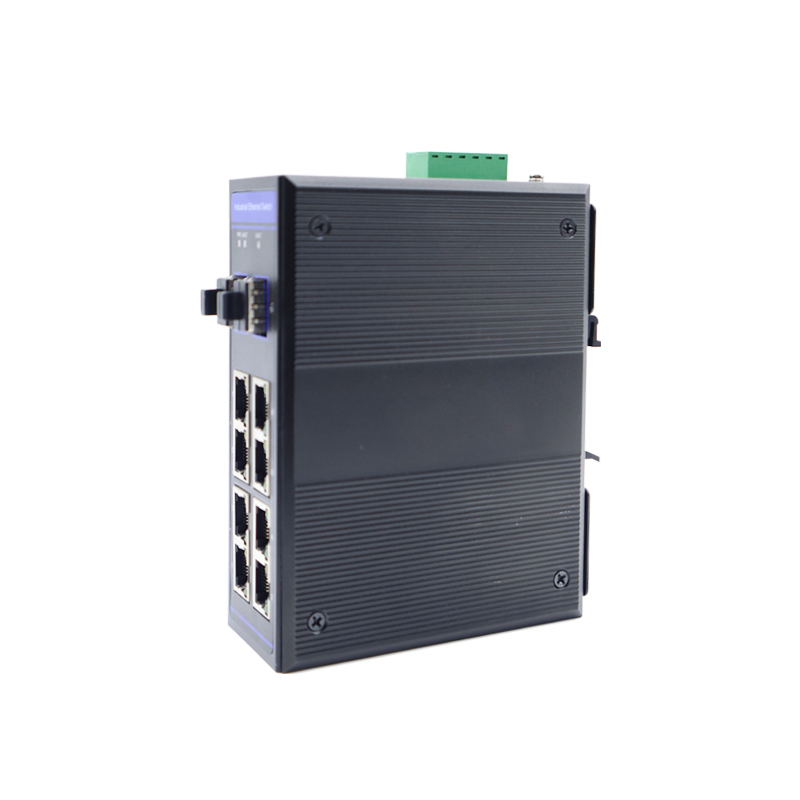
In the world of network infrastructure, enterprise switches are the cornerstone, facilitating seamless communications and data flow within an organization. While these devices may look like black boxes to the uninitiated, closer inspection reveals a carefully engineered assembly of various components, each playing a critical role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Let’s take a closer look at the inner workings of enterprise switches and uncover the complex tapestry of components that make up the backbone of modern networking solutions.
1. Processing capacity:
At the heart of every enterprise switch is a powerful processor that serves as the command center for all operations. These processors are typically high-performance CPUs or specialized ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits) that perform critical functions such as packet forwarding, routing, and access control with lightning speed and accuracy.
2. Memory module:
Memory modules, including RAM (random access memory) and flash memory, provide the switch with the necessary resources to store and process data. RAM facilitates quick access to frequently used information, while flash memory serves as persistent storage for firmware, configuration files, and operational data.
3. Ethernet port:
Ethernet ports form the physical interface through which devices connect to the switch. These ports are available in a variety of configurations, including traditional copper RJ45 ports for wired connections and fiber optic interfaces for long-distance and high-speed network requirements.
4. Exchange structure:
The switching fabric represents the internal architecture responsible for directing data traffic between connected devices. Using complex algorithms and table lookups, the switching fabric efficiently routes packets to their intended destination, ensuring minimal latency and optimal bandwidth utilization.
5. Power supply unit (PSU):
Reliable power supply is essential for uninterrupted switching operation. The power supply unit (PSU) converts incoming AC or DC power to the appropriate voltage required by the switching components. Redundant PSU configurations provide additional resiliency, ensuring continued operation in the event of a power failure.
6. Cooling system:
Given the intensive processing demands of enterprise switches, an efficient cooling system is critical to maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating. Heat sinks, fans, and airflow management mechanisms work together to dissipate heat generated by active components and ensure switch performance and service life.
7. Management interface:
Enterprise switches have management interfaces such as a web-based dashboard, command line interface (CLI), and SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) agents that enable administrators to remotely configure, monitor, and troubleshoot network operations. These interfaces enable IT teams to maintain network integrity and proactively resolve emerging issues.
8. Security features:
In an era of escalating cyber threats, strong security capabilities are critical to protecting sensitive data and network infrastructure. Enterprise switches integrate advanced security mechanisms, including access control lists (ACLs), VLAN segmentation, encryption protocols, and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), to harden network perimeters against malicious activity.
in conclusion:
From processing power to security protocols, every component in an enterprise switch plays a critical role in delivering reliable, high-performance networking solutions. By understanding the complexity of these components, organizations can make informed decisions when selecting and deploying network infrastructure, laying the foundation for an agile, resilient, and future-proof IT ecosystem.
Post time: May-09-2024